we bring your ideas to life

A Look into the Phenomenon of Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0 is the current trend of automation and data exchange in manufacturing technologies. It includes cyber-physical systems, the Internet of Things, cloud computing, and cognitive computing. Industry 4.0's main objectives are to create more flexible, efficient, and cost-effective manufacturing processes. It also seeks to create a more connected and intelligent manufacturing environment that can respond quickly to changing customer demands.
History
The manufacturing of products is as old as human beings. In earlier days, products such as weapons, clothing, shelter, and food were all produced by hand using simple tools and equipment. Subsequently, man has learned to use animal power and later the wind and running water. Eventually, man has learned to transform energy from one form to another. The extensive use of mechanical power is an outstanding attribute of human advancement.
Great advancements have now been made in the production industry; new technologies have been introduced in the modern industry, leading to a significant change in the manufacturing processes carried out. These developments enable us to produce items on a large scale and for commercial purposes.
This process of transitioning from handmade products to a manufacturing industry that uses machines and new technologies is referred to as the Industrial Revolution.
The history of industrial revolutions can be traced back to the late 18th century.
Since the 1800s, we have experienced four industrial revolutions. Each was powered by disruptive new technology the mechanics of the steam engine, the innovation of the assembly line, and the speed of the computer. They were called industrial revolutions because the technological advancement that drove them didn’t just improve productivity and efficiency a little bit, but it completely revolutionized the manufacturing process.
The transitions of the industrial revolution were mainly evident in the United States, Great Britain, and Europe. However, by the 20th century, the revolution had already spread to more or less all parts of the world, bringing a new era of modern industry. These changes happened gradually, with each stage enhancing into a better modern and more innovative stage.
So far, we have gone through three industrial revolutions and now, we are in the middle of the fourth industrial revolution known as industry 4.0.
Stages of the industrial revolution:
The first industrial revolution began in England in the 18th century, from around 1760 to 1840. This period saw the introduction of new technologies and innovations, such as the steam engine and the power loom, which significantly increased productivity and efficiency in manufacturing and other industries and allowed for mass production.
The second industrial revolution began in the 19th century, around 1870. It mainly occurred in Germany, America, and Britain. This period was also known as the “Technological Revolution” era. It mainly involved industrial processes that used machines powered by electrical energy. During this time, new technologies such as the internal combustion engine, the telephone, and the electric motor were developed and adopted, leading to further increases in productivity and efficiency. The second revolution also saw the rise of mass production techniques, such as assembly line manufacturing, which greatly increased the speed and scale of production.
The Third Industrial Revolution also known as the Digital Revolution began in the late 20th century around 1970. This period has seen the widespread adoption of digital technologies such as computers, the internet, and automation, leading to further productivity and efficiency. This revolution also has a strong focus on data and information technology. The third industrial revolution began through partial automation; a technological process that was achieved using simple computers and Programmable Logic Controllers.
[It is important to note that the third Industrial revolution (Industry 3.0) is still present even today. Most factories and production industries are currently at this evolution level.]
The Fourth Industrial Revolution began in the 21st century around 2010, it builds on the third revolution and is marked by the emerging technologies of Artificial Intelligence, Robotics, Nanotechnology, quantum computing, biotechnology, Internet of Things, Blockchain and 3D printing.
We are now in the Fourth Industrial Revolution also known as Industry 4.0, which is the latest phase in the ongoing technological advancement of manufacturing and industry.
What is Industry 4.0?
Industry 4.0 is the fancy name given to the fourth Industrial revolution. It is sometimes spelt as Industrie 4.0, this is the German translation of Industry so both can be used interchangeably.
Industry 4.0 was coined in 2011 by a German initiative by the Federal government in association with some universities and private firms to increase productivity and efficiency in the manufacturing sector.
The term was initially introduced by the German government in its attempt to promote digitisation. Their version was “Industrie 4.0” or simply “I4”.
It was used during the Hannover Fair in 2011. Something that initially started as a great idea quickly turned into action: The German government created a working group in 2012 that was meant to create guidelines which would then be implemented at a federal level.
Americans prefer to call this concept a smart factory and Europeans call it Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0 concepts and technologies can be applied across all types of industries, including discrete and process manufacturing, as well as oil and gas, mining, and other industrial segments.
A Cyber-physical system plays a vital role in Industry 4.0 and is changing the face of the industry. It again is a fancy name for the physical systems with electronics embedded in them for making them intelligent.
Definition:
Industry 4.0 is the integration of data, artificial intelligence, machinery, and communication to create an efficient industrial ecosystem that is not just automated but intelligent. Industry 4.0 is the process of embedding intelligence and connectedness in manufacturing and supply chain to provide satisfying products and services.
Industry 4.0 refers to the integration of advanced technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and big data analytics into manufacturing and industrial processes. This integration is designed to improve efficiency, productivity, and flexibility, while also enabling greater customization and faster time-to-market for products. Industry 4.0 also involves the use of advanced robotics and automation, as well as the integration of virtual and augmented reality into the manufacturing process. Overall, the goal of Industry 4.0 is to create “smart factories” that are highly connected, data-driven, and capable of adapting to changing market conditions in real time.
The technologies driving Industry 4.0:
- Internet of Things (IoT): The IoT refers to the interconnectedness of physical devices, such as industrial machines and equipment, that are equipped with sensors and software that allow them to communicate and share data. This enables real-time monitoring and control of industrial processes, and the ability to quickly respond to changes in production conditions.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML are used in Industry 4.0 to analyze large amounts of data generated by IoT devices, and make predictions and decisions based on that data. This allows for improved efficiency and automation of manufacturing processes as well as the ability to quickly adapt to changing market conditions.
- Big Data Analytics: With the large amounts of data generated by IoT devices, big data analytics are used to extract valuable insights from this data, which can be used to optimize production processes, improve product quality, and reduce costs.
- Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS): CPS are the integration of physical and cyber systems, which allow for the seamless integration of the physical world with digital systems. They enable the real-time monitoring and control of industrial processes and make it possible to optimize production and logistics.
- Cloud Computing: Cloud computing allows for the storage and processing of large amounts of data, as well as the ability to access that data from anywhere. This enables the sharing of data across different locations and systems, and the ability to scale resources up or down as needed.
- Robotics and Automation: Robotics and automation are used to improve the efficiency and flexibility of manufacturing processes, as well as to reduce human error and increase productivity.
- Virtual and Augmented Reality (VR/AR): VR and AR are used in Industry 4.0 to improve training and education, as well as to assist in the design and development of new products. They also allow for remote monitoring and maintenance of industrial equipment, and the simulation of complex production scenarios.
- 5G technology: 5G networks provide faster data transfer rates and lower latency than previous generations of cellular networks, which enables the real-time communication and control of IoT devices and other Industry 4.0 technologies. This allows for more efficient and responsive production processes and improved automation.
- Blockchain: Blockchain technology provides a secure and tamper-proof way to store and share data, making it suitable for use in supply chain management, logistics, and other areas where transparency and traceability are important.
- Advanced Robotics: With the development of advanced robotics technology, robots are becoming more versatile and autonomous, which allows them to work alongside humans, or in place of them. This enhances the efficiency, speed, and precision of the manufacturing process.
- Advanced Materials: Industry 4.0 is characterized by the use of advanced materials in manufacturing, such as carbon-fibre composites, which are used in aircraft and automotive industries. The use of advanced materials can reduce weight and increase strength, which can improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions.
- Additive Manufacturing: Also known as 3D printing, this technology allows for the creation of complex parts and structures quickly and economically. This technology is used in aerospace, automotive, and medical industries, to name a few.
Overall, the technologies driving Industry 4.0 are aimed at creating a highly connected, data-driven, and automated manufacturing environment that is capable of quickly adapting to changing market conditions. This is expected to result in increased efficiency, productivity, and flexibility, as well as the ability to customize products to meet the specific needs of individual customers.
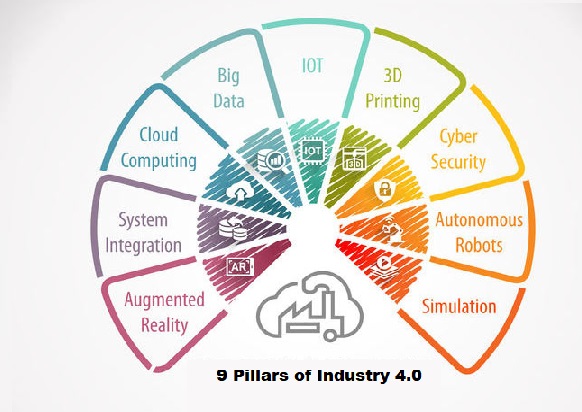
Nine Pillars of Industry 4.0:
At the core of Industry 4.0 are nine pillars, each of which plays a critical role in the transformation of manufacturing and industrial processes. These pillars are:
- Big Data and AI analytics:In Industry 4.0, Big Data is collected from a wide range of sources, from factory equipment and Internet of Things (IoT) devices to ERP and CRM systems. Analytics powered by artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are applied to the data in real time to make smart decisions in every area of business based on predictive analysis and statistical algorithms.
- The Industrial Internet of Things: The Industrial Internet of Things refers to using the Internet to connect all smart devices. The Industrial Internet of Things is so central to Industry 4.0 that the two terms are often used interchangeably. Most physical things in Industry 4.0 devices, robots, machinery, equipment, and products use sensors and RFID tags to provide real-time data about their condition, performance, or location. This technology helps run smoother supply chains, rapidly design, and modify products, prevent equipment downtime, stay on top of consumer preferences, track products and inventory, and much more.
- Horizontal and vertical integration:The backbone of Industry 4.0 is horizontal and vertical integration. With horizontal integration, processes are tightly integrated on the production floor, across multiple production facilities, and the entire supply chain. With vertical integration, the data flows freely from the shop floor to the top floor and back.
- Cloud computing: Cloud computing is the great enabler of Industry 4.0 and digital transformation. Today’s cloud technology goes way beyond speed, scalability, storage, and cost efficiencies. It provides the foundation for the most advanced technologies from AI and machine learning to the Internet of Things and gives businesses the means to innovate. The data that fuels Industry 4.0 technologies resides in the cloud, and the cyber-physical systems at the core of Industry 4.0 use the cloud to communicate and coordinate. With the increased utilization of technology and data sharing, cloud computing has now become the first and foremost choice of organizations for enhanced computing power. Cloud computing allows companies to store and share multitudes of data and information.
- Autonomous robots:With Industry 4.0, a new generation of autonomous robots is emerging. Programmed to perform tasks with minimal human intervention, autonomous robots vary greatly in size and function, from inventory scanning drones to autonomous mobile robots for pick and place operations. Equipped with cutting-edge software, AI, sensors, and machine vision, these robots are capable of performing difficult and delicate tasks – and can recognize, analyze, and act on the information they receive from their surroundings. Autonomous robots are likely the new future. These collaborative robots are designed to fill the gaps between traditional robots and human beings. Autonomous robots are the new smarter robots that can easily interact and learn from humans.
- Augmented Reality: Augmented reality, which overlays digital content in a real environment, is a core concept of Industry 4.0. With an AR system, employees use smart glasses or mobile devices to visualize real-time IoT data, digitized parts, repair or assembly instructions, training content, and more when looking at a physical thing – like a piece of equipment or a product. AR is still emerging but has major implications for maintenance, service, and quality assurance as well as technician training and safety.
- Simulation/digital twins: A digital twin is a virtual simulation of a real-world machine, product, process, or system based on IoT sensor data. This core component of Industry 4.0 allows businesses to better understand, analyze, and improve the performance and maintenance of industrial systems and products. An asset operator, for example, can use a digital twin to identify a specific malfunctioning part, predict potential issues, and improve uptime.
- Cybersecurity: With increased connectivity, networking and integration, it’s increasingly important for businesses to ensure high levels of cybersecurity, as the risk of a potential cyber-attack grows alongside. A simple security breach could be able to do unimaginable damage to business operations.
- Additive manufacturing/3D printing: Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, is another key technology driving Industry 4.0. 3D printing was initially used as a rapid prototyping tool but now offers a broader range of applications, from mass customization to distributed manufacturing. With 3D printing, the parts and products can be stored as design files in virtual inventories and printed on demand at the point of need reducing both transportation distances and costs.
These pillars are designed to enhance the efficiency, flexibility, and intelligence of industrial processes and manufacturing operations. They are being implemented in various industries such as automotive, aerospace, and healthcare and also in agriculture, mining, and construction.
Benefits of Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0 has the potential to bring many benefits, including:
Increased Efficiency
Industry 4.0 utilizes automation, data exchange and smart technologies to increase productivity and efficiency.
Customization
By leveraging data and technology, Industry 4.0 can offer customers, personalized products and services that meet their specific needs.
Improved Quality
The use of sensors and automation technology helps to increase the quality of products and services by reducing the risk of human error.
Increased Flexibility
Industry 4.0 enables companies to quickly adapt to changes in demand, production processes and supply chains.
Cost Savings
The increased efficiency and automation of production processes can lead to significant cost savings for companies.
Better Data Management
Industry 4.0 generates large amounts of data that can be analyzed and used to inform decision-making and improve overall operations.
Sustainability
Industry 4.0 has the potential to reduce waste, increase resource efficiency and lower the environmental impact of production processes.
Improved Safety
Industry 4.0 technologies, such as robotics and autonomous systems, can help to reduce workplace accidents and improve overall safety in industrial environments.
Enhanced Collaboration
The use of cloud-based technologies and the Internet of Things (IoT) enables better collaboration between companies, suppliers, and customers, leading to improved supply chain management and faster innovation.
Predictive Maintenance
By using predictive analytics and monitoring technologies, Industry 4.0 allows companies to detect potential problems and perform maintenance before equipment failures occur, reducing downtime and improving overall equipment reliability.
Increased Agility
Industry 4.0 enables companies to quickly respond to changes in the market and adjust production processes, accordingly, improving their competitiveness and ability to innovate.
Better Customer Experience
By using data and advanced technologies, Industry 4.0 can provide a more personalized and seamless customer experience, improving customer satisfaction and loyalty.
In conclusion, Industry 4.0 offers numerous benefits to companies and industries, including increased efficiency, customization, quality, and cost savings. By leveraging data and technology, companies can drive innovation, improve their operations, and enhance their overall competitiveness.
One of the key benefits of Industry 4.0 is increased efficiency and productivity. With the integration of advanced technologies, machines can work together to optimize production, reducing downtime and increasing uptime. Predictive maintenance can be used to proactively identify and fix issues before they occur, reducing the risk of unexpected downtime.
Another benefit of Industry 4.0 is the ability to produce customized products with short lead times. With the use of digital twins, production processes can be simulated and optimized before they are implemented, reducing the time and resources required to bring new products to market.
One of the key drivers of Industry 4.0 is the growing availability of data. With the proliferation of connected devices, sensors, and machines, large amounts of data are being generated in real-time. This data can be analyzed to gain insights into production processes, identify inefficiencies, and adjustments to optimize production.
Another driver of Industry 4.0 is the increasing need for customization and flexibility in manufacturing. With the rise of e-commerce and the decline of retail, customers expect to be able to order customized products with short lead times. Industry 4.0 technologies enable the creation of highly flexible and adaptable production processes, where machines can be quickly reconfigured to produce different products.
One of the challenges of Industry 4.0 is the need for a skilled workforce. With the integration of advanced technologies, the skills required for manufacturing and industrial processes are changing. Companies need to invest in training and development programs to ensure that their employees have the skills necessary to work with Industry 4.0 technologies
Another challenge of Industry 4.0 is cybersecurity. With the increasing connectivity of machines and systems, the risk of cyber-attacks increases. Companies need to implement robust cybersecurity
measures to protect their systems and data from unauthorized access and breaches. This includes measures such as firewalls, encryption, and access controls.
Tips and best practices for implementing Industry 4.0
- Develop a clear roadmap
Before implementing Industry 4.0, companies should develop a clear roadmap outlining the steps they will take to achieve their goals. This should include identifying the areas where Industry 4.0 can bring the most value, as well as the resources and budget required to implement it. - Start small
Companies should start small and focus on one or two areas where Industry 4.0 can bring the most value. This allows them to gain experience and learn from the implementation before expanding to other areas. - Invest in the right technologies
Companies should invest in technologies that are relevant to their operations and that can bring the most value. This includes things like IoT, AI, and ML. - Invest in talent
Companies should invest in the development of a skilled workforce, through education and training programs. This is critical for the successful implementation of Industry 4.0, as it requires a workforce that is skilled in advanced technologies. - Focus on data
Companies should focus on the collection and analysis of data, as it is critical for the success of Industry 4.0. This includes things like data governance, data quality, and data security. - Collaborate with partners
Companies should collaborate with partners, such as technology providers and other companies, to share knowledge and experience. - Continuously monitor and improve
Companies should continuously monitor and improve their Industry 4.0 operations, using data and feedback to identify areas for improvement. - Embrace change
Implementing Industry 4.0 requires a mindset of continuous improvement and a willingness to embrace change. Companies should be open to new ideas, technologies, and ways of working. - Prioritize cybersecurity
With Industry 4.0 comes, an increased risk of cyber-attacks, therefore, companies should prioritize cybersecurity and implement measures such as firewalls, encryption, and access controls to protect their systems and data. - Compliance with regulations
Companies should ensure that their Industry 4.0 implementation is compliant with all relevant regulations, including data privacy, data protection and cybersecurity regulations.
By following these tips and best practices, companies can successfully implement Industry 4.0 and reap the benefits it brings, such as increased efficiency, productivity, and flexibility in their operations. It’s important to remember that the implementation of Industry 4.0 is a journey, not a destination and companies should be prepared for continuous learning and improvement.
Industry 4.0 is already having a significant impact on the manufacturing industry, and its impact is expected to spread to other industries as well, such as healthcare, agriculture, mining, and construction. Companies that embrace the nine pillars of Industry 4.0 will be well-positioned to take advantage of the opportunities it presents and thrive in the new industrial landscape.
Here is a list of some companies that have implemented Industry 4.0 or Industry 4.0 technologies:
- Siemens
- Bosch
- ABB
- Schneider Electric
- Rockwell Automation
- GE Digital
- PTC
- Cisco
- Microsoft
- SAP
Here is a list of some companies manufacturing diesel engines and diesel generators that have implemented Industry 4.0 technologies:
- Caterpillar Inc.
- Cummins Inc.
- MTU Onsite Energy
- Wartsila
- SDMO Industries
- Kohler Power Systems
- John Deere Power Systems
Conclusion:
In conclusion, Industry 4.0 represents a new era of manufacturing, characterized by the integration of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, IoT, and automation. This fourth industrial revolution has the potential to revolutionize the way we work, live, and do business, creating a more connected and efficient world. Businesses that adopt these innovative technologies, can gain a competitive advantage, with improved productivity, lower costs, and better customer experiences. As technology continues to evolve, Industry 4.0 will be a driving force in shaping the future of manufacturing and beyond.
However, the implementation of Industry 4.0 also brings new challenges, such as the need for a skilled workforce, and cybersecurity. The implementation of Industry 4.0 can also have a significant impact on the workforce. With the increasing use of collaborative robots and AI, some jobs may become obsolete, while new jobs may be created. Companies need to be aware of these changes and plan accordingly, to ensure that their workforce is prepared for the future.
While the concept works amazingly for bigger systems, it might not be ideal for smaller enterprises. Its effect will also vary from industry to industry.
Some are unwilling to make the shift due to preconceptions or conservatism. However, as we go forward, it seems that Industry 4.0 will not only represent a small technical benefit, but it will become a requirement to stay in business.
In this post, we have tried to compile all freely available information on various internet sites, so ultimately you do not need to spend your time searching for it.
You can reach out to us at www.sgpowerplus.com or you can send us an email at sg@suhasghatnekar.com, or you can fill out our Contact Form with any questions or inquiries and we will get right back to you.
Did you find this blog post helpful?
If so, please share it with your friends and colleagues or share it on LinkedIn, Twitter or Facebook. This will help us improve our blog post readership. Thank you!!
(References for information and images: Thank you Openai, circuit digest, sap, pixabay and istock.)
Suhas Ghatnekar
The author is an Electrical engineer from the National Institute of Technology Rourkela India, an enterprising techno-commercial professional in the
field of diesel engines and diesel generators.

